Cookiebot-Enhanced Website Technology

Cookiebot-Enhanced Website Technology
The True Impact of COVID On Employees: 1-In-4 Want to Quit Their Jobs Because of Poor Business Processes
December 02, 2020

COVID-19 Technology Survey by ABBYY shows two-thirds of businesses adopted AI during lockdown
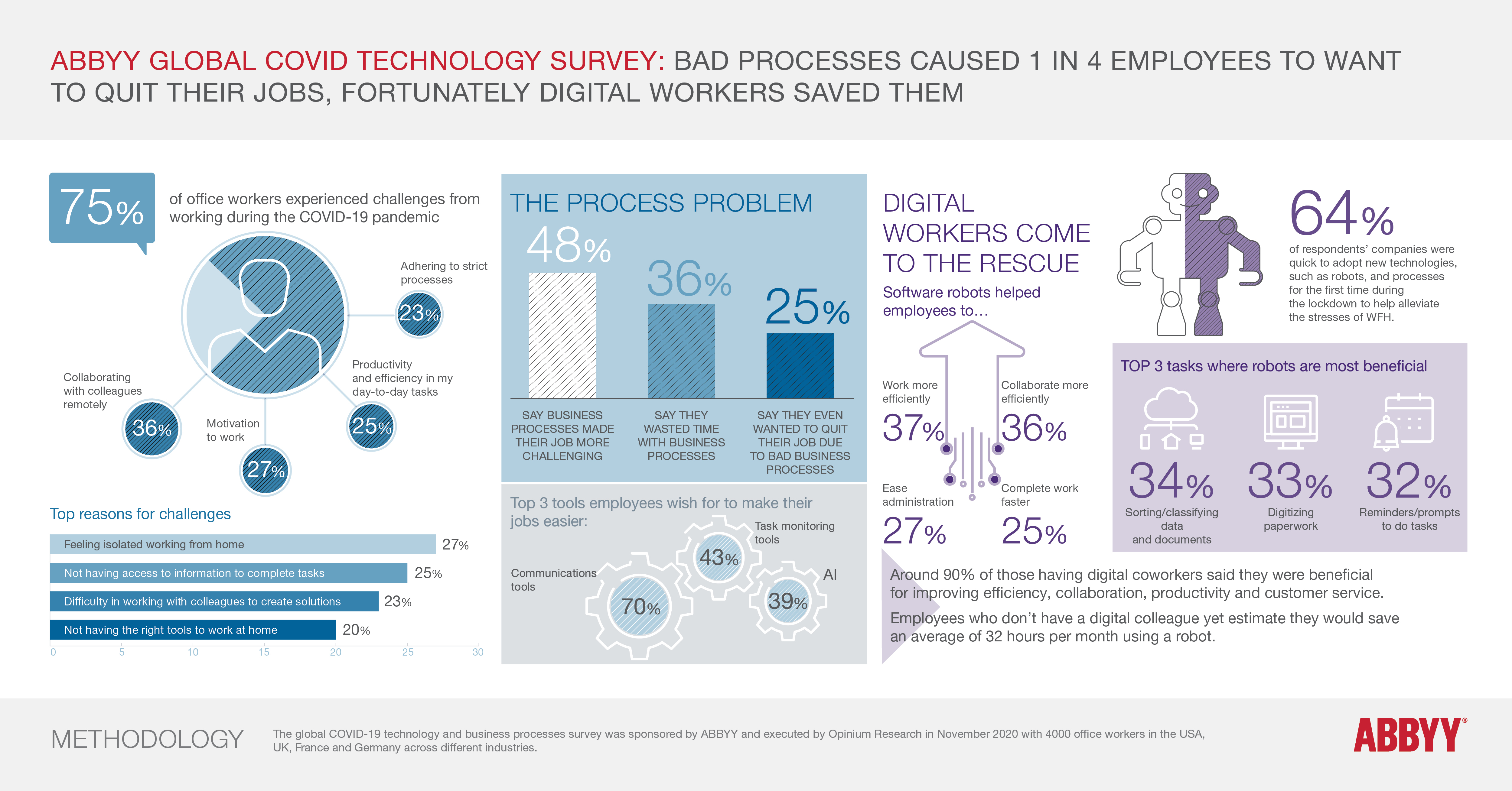
Working from home during the pandemic has taken its toll on many workers, with one in four wanting to quit because of poor business processes, according to a new survey. The global COVID-19 Technology and Business Processes Survey discovered nearly half of staff (48%) blamed bad processes for making their job more challenging – with a third saying they waste time.
Luckily for some, 64% of companies were quick to adopt new technologies and processes for the first time during the lockdown to help alleviate the stresses of remote working, according to the survey, carried out by Opinium Research in November 2020 on behalf of digital intelligence company ABBYY .
Those using digital workers – aka robotic process automation (RPA) software robots – estimate that they save them an average of 26 hours a week in productivity.
The survey investigating the impact of COVID-19 and automation technologies on office workers included 4,000 staff in 20 industries across the U.S., UK, France, and Germany.
Other key findings include:
- Three-quarters (74%) of workers feel they experienced challenges since the pandemic began.
- When identifying the cause of their biggest challenges, 40% of workers blame a lack of information on solutions or tasks, while 32% blamed not having the right IT tools.
- In asking what tools could make their job better, the top three answers were communications tools (70%), task monitoring (43%), and AI (39%).
- Software robots are being used by 46% of respondents, who reported that they spend up to two (2) hours a day with their digital co-worker.
- Of those working with digital co-workers, 34% said they were most helpful at sorting and classifying data and documents.
- Those who wished they had a digital co-worker said they would use them for digitizing paper, prompts, and classification purposes and could save 54 days per year using a digital colleague.
As the survey results show, organizations continue to face rising challenges when it comes to quickly and accurately processing content such as documents, forms, images, and email communications. It can require an enormous amount of manual work to find specific information in a document, perform data entry, and route the document for review and approval. The survey revealed that 76% of tools used to help with processes, digitizing the automation and content within paper, and onboarding new clients were deemed successful for respondents, including tools for monitoring employees’ tasks. This points to the growing trend of many organizations that are now turning to technologies like content intelligence, process mining, and task mining to support their digital transformation efforts and discover and address the inefficiencies of business processes in order to optimize the productivity of their staff and meet customer expectations.
“During 2020, we saw a forced modernization of technology to meet an increasingly remote standard of doing business. We also saw the consequences of introducing new technologies too quickly and not fully understanding how they impact the entire business process workflow – they ended up frustrating employees and impacting their productivity,” said Bruce Orcutt, Senior Vice president of Product Marketing at ABBYY. “In order to meet new demands, businesses need to know where their inefficiencies lie and how they can fix them before considering new automation tools. It’s exactly why there is a surge in leveraging process intelligence tools that also encapsulate how workers complete their tasks. Additionally, incorporating AI into documents allows digital co-workers to augment human intelligence for more timely and smarter business decisions.”
About ABBYY
ABBYY empowers organizations to gain a complete understanding of their business processes and the content that fuels them with its Digital Intelligence platform. ABBYY technologies are used by more than 5,000 companies, including many of the Fortune 500, and is recognized for its leadership in Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) and Process Discovery & Mining for driving significant impact where it matters most: customer experience, effectiveness, profitability and competitive advantage. ABBYY is a global company with offices in 14 countries. For more information, visit www.abbyy.com or visit us on social on LinkedIn , Twitter and Facebook .
ABBYY and the ABBYY Logo are either registered trademarks or trademarks of ABBYY Software Ltd. Other product names mentioned herein may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective owners and are hereby recognized.
ABBYY Editorial Contact
Gina Ray, APR
949-370-0941
[email protected]
Connect with us
Also read:
- [New] 2024 Approved Flash Frame Filmmaking Script
- [New] 2024 Approved Zoom Optimization Techniques for Windows 11 Users
- [New] Ps5 Expansion Leading External Drives Unveiled for 2024
- Differentiating NLP From ML Basics
- Enhanced Site Tracking with the Power of Cookiebot Technology
- Enhanced User Experience with Advanced Analytics: Powered by the Leading Cookiebot Solutions
- Enhanced User Experience with Automated Consent Management: Powered by Cookiebot
- Enhanced User Experience with Automated Personalization Using Cookiebot
- Enhanced User Experience with Cutting-Edge Cookiebot Technology
- Enhanced Web Tracking and Personalization Through Cookiebot Integration
- Free Online Conversion: Transforming WebM Files Into MPEG Format with Ease
- Inside Look: Our Experience with Le Chat by Mistral AI Vs. The Power of ChatGPT
- Troubleshoot a Non-Responsive Huion Pen with These 5 Effective Techniques
- Title: Cookiebot-Enhanced Website Technology
- Author: Brian
- Created at : 2024-10-04 19:40:28
- Updated at : 2024-10-05 16:22:56
- Link: https://discover-best.techidaily.com/cookiebot-enhanced-website-technology/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.